Introduction to Alzheimer’s Disease
Overview
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative condition where brain cells gradually lose function and die, leading to the destruction of memory, thinking skills, and the ability to perform even basic tasks (National Institute on Aging, 2023). Neuroinflammation refers to the inflammatory response within the brain or spinal cord, which can lead to immune cell recruitment, edema, tissue damage, and potential cell death (DiSabato et al., 2016).
Alzheimer’s progresses through stages, generally starting with preclinical brain changes, advancing to mild cognitive impairment (MCI), and eventually severe dementia, where patients lose the ability to communicate and perform daily functions (Mayo Clinic, 2023).
Despite ongoing research, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s, emphasizing the need for effective management strategies (Kumar et al., 2022). This gradual decline creates a significant emotional and physical burden on individuals and caregivers, making Alzheimer’s a pressing public health issue.
Misconceptions
It is commonly believed that memory loss is a normal part of aging, but significant memory loss and cognitive decline, like those seen in Alzheimer’s, are not. Forgetfulness is part of aging, but Alzheimer’s shows signs of persistent forgetfulness and individuals may fail to recognize familiar faces and places. Another misconception is that Alzheimer’s only affects older adults.
While it is more common in individuals who are over 65, early-onset Alzheimer’s can affect people as young as their 30s or 40s (National Institute on Aging, 2022). This “old person’s disease” perspective often leads to delayed diagnoses and missed symptoms.
Moreover, according to the National Institute on Aging (2023), although Alzheimer’s Disease has a major genetic component, other factors such as environmental conditions and lifestyle choices impact likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s. By raising awareness, the importance of recognizing these misconceptions can offer early intervention and better support.
Rationale for Learning Resource
Alzheimer’s disease has a widespread impact on patients, families, and caregivers all over the world. Although there is currently no cure, early detection and awareness can improve the quality of care and preparation for people who might be affected by this.
A learning resource can help educate the younger population to recognize the early signs of Alzheimer’s using a cognitivism approach, preparing them for the physical, emotional, and financial challenges they may face when caring for a loved one with the disease.
This is done by teaching them about the disease in the form of a blog post, and walking them through various sources of information, performing activities, and undergoing assessments to ensure understanding.
Learning Context / Target Audience
The learning resource is designed for high school students ages 13 to 18, helping them explore and understand Alzheimer’s disease. The course will be offered in English and provides guidance to available support services within the community for students who may have a loved one affected by the disease.
Additionally, the resource will be accessible to anyone with access to a computer or mobile phone and they can access the website and tests online. Students who might be working part-time can do the coursework in their own time and can test themselves using the assessments provided on the platform. This flexibility allows students to understand and empower themselves on learning about Alzheimer’s disease, while accommodating their busy schedules.
Platform for Hosting
The learning resource will be hosted on a user-friendly website that is Notion. The website will offer content, quizzes, and Kahoot games that are accessible across devices. Additional features on videos will include closed captioning thereby making the resource more inclusive for users with disabilities.
Accessibility and Inclusion
Learning Context
This course focuses on teaching high school children on Alzheimer’s with a basic foundation of biology. The course will teach the content through direct instruction which allows “teachers [to deliver] detailed, guided, and explicit instructions” for learners to understand the complex disease of Alzheimer’s (Tremblay, 2023). It allows for students to understand the beginning and later stages of the disease, along with pain management and treatment. Having a step-by-step process can allow engagement in the students to be invested in the topic.
To expand on Alzheimer’s core concepts, the definition of the disease must be clearly outlined. According to the National Institute on Aging (2023), Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative condition in which it slowly damages the brain, making it harder to remember things, think clearly, and handle daily tasks. Over time, it gets worse, affecting even the simplest activities.
There are many aspects that surround Alzheimers, however the main topics that the course offers involves the stages, management, and impact of the disease. These topics will be covered in this course and will teach the student the core concepts of Alzheimer’s disease.
Inclusive Design
All learners must have their needs met and in order to do so, applying the universal design for learning (UDL) approach will identify and reduce any potential learning barriers for students. The universal design for learning approach is a framework that helps “improve and optimize teaching and learning for all people based on scientific insights into how humans learn” (CAST, Inc.).
Lastly, inclusion refers to the integration of both typically developing and special needs children in the same learning environment, fostering co-learning while ensuring a balanced and supportive atmosphere for all students (Tanwar, 2018).
Some of the main barriers that can make it difficult for people with disabilities to engage with the materials include visuals, auditory, and possible fast-paced or overwhelming assessments (i.e. Quizlets). To address visual and auditory barriers, we provided a list of YouTube videos for students to watch, an illustrative diagram, and Quizlet.
This platform allows for subtitles which the learner can customize the appearance (i.e. contrast, font, size). Along with these adjustments are multilingual support where learners can change the captions to another language they understand the most and can retain the material better.
As for the diagram provided in the course, this will allow for students with “visual impairments to increase the efficacy of their learning” (Tanwar, 2018). This will cater to students who grasp concepts better through visuals than through text and allows for complex concepts to be simplified, thereby making it easier to process.
Furthermore, the colors and easy-to-read fonts avoid clutter and highlight the main ideas from the course material for the students. Lastly, Quizlet allows options where students can use text-to-speech and adjust the color contrast adjustment for visually impaired users, as well as the dark mode option which reduces eye strain for low-vision users. By addressing accessibility barriers in learning material, this ensures that all students can engage with the course material effectively.
Affordances of Technology
Technology plays a critical role in enhancing education by increasing accessibility, personalizing learning experiences, and fostering engagement. Digital tools such as online quizzes, interactive videos, and collaborative platforms allow students to interact with content in dynamic ways that traditional methods may not support. However, it is essential to critically evaluate how technology is implemented in learning environments.
While platforms like Kahoot and Notion make assessments and content delivery more engaging, the ethical implications of technology in education, including issues of surveillance, accessibility, and commercialization, should not be overlooked. By thoughtfully integrating technology, educators can create an inclusive and effective learning experience that prioritizes student agency and understanding.
Assessment Plan
Core Concepts
- Progression and Impact of Alzheimer’s Disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that significantly impacts cognitive function, memory, and daily life, affecting not only individuals but also families and caregivers. Understanding the stages of Alzheimer’s (preclinical, mild cognitive impairment, mild dementia, moderate dementia, and severe dementia) is crucial for early recognition and effective management. - Early Detection and Management
While there is no cure for Alzheimer’s, early detection and management of symptoms can improve quality of life. Learning about available treatments, lifestyle interventions, and the importance of early diagnosis can empower individuals and communities to take action.
Essential Questions
Question 1: How can you determine which stage of Alzheimer’s Disease an individual has?
Question 2: How can you tell if a symptom (such as facial blindness) is caused by Alzheimer’s Disease, or some other cause(s)?
Question 3: What is the best treatment method for Alzheimer’s Disease?
Learning Outcomes
- Identify the 5 stages of Alzheimer’s Disease.
- Describe the symptoms and progression of Alzheimer’s Disease.
- Understand available treatment options of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Sources To Study
- Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease:
- Symptoms and Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease:
- Current Treatments and Emerging Therapies:
Learning Activities
Interaction Design
the following learning activities aim to improve understanding of the topic and further prepare learners for the assessment portion of the Interactive Learning Blueprint. The assessments follow a learner-content format, encouraging students to interact with the material directly, and generate their own ideas and understanding as a result.
Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease
To help you get a better understanding of the learning outcomes, the diagram below demonstrates the five stages of Alzheimer’s. Please take a look at the diagram, noting the difference between the stages.
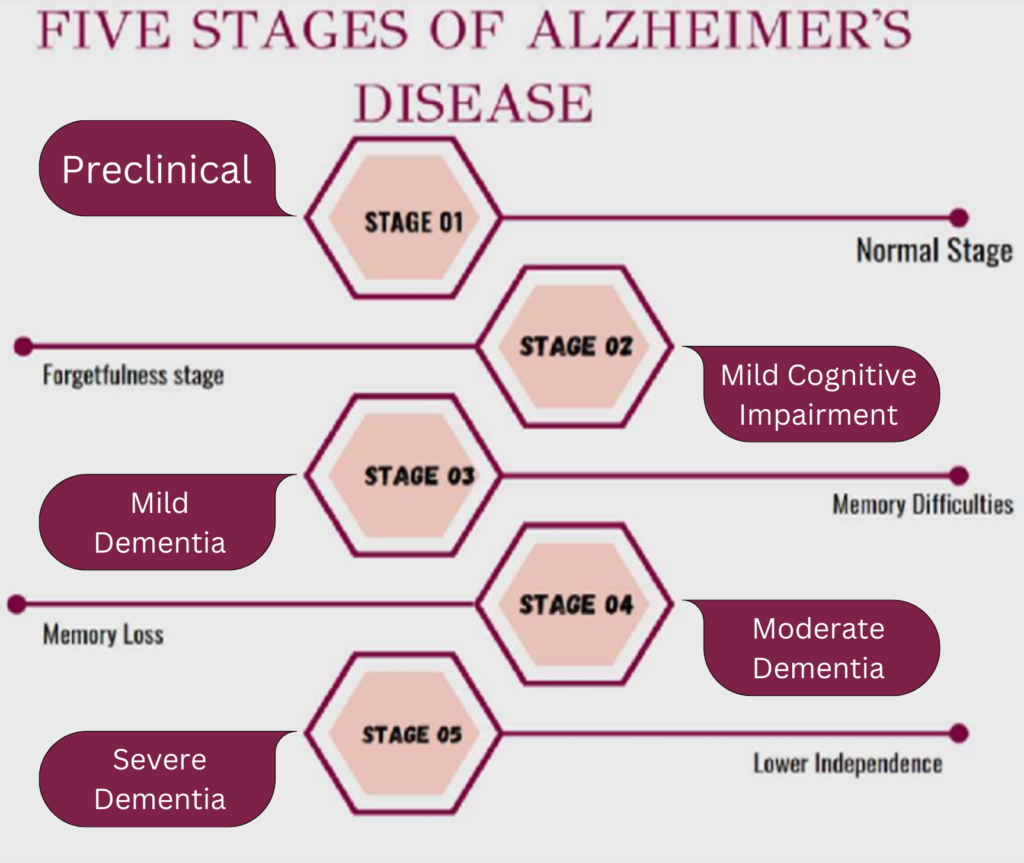
The first stage is Preclinical Alzheimer’s, where an individual does not experience any symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease, and is relatively healthy (barring other potential health issues).
In the second stage, individuals usually experience some memory issues, forgetting recent events. In the third stage, it becomes apparent that the individual is experiencing problems with memory and thinking.
People in the third stage may experience changes in personality and behavior, trouble with problem solving and critical thinking, and issues locating lost items (such as a phone or TV remote).
In the fourth stage, personality changes become more apparent, further reducing critical thinking abilities, and causing greater memory loss. In this stage, individuals may require assistance with daily activities (from family members or medical professionals) such as being clothed or using the bathroom.
In the fifth and final stage, individuals lose the ability to communicate or even move, requiring assistance with most daily tasks. Overall, people with Alzheimer’s live around 3-11 years after diagnosis, but some live for 20 or more years. Eventually, people succumb to pneumonia, malnutrition or dehydration due to the inability to swallow in the late stages of the disease.
Symptoms and Treatments
The video below talks about Alzheimer’s Disease. The video seeks to provide learners with information about Alzheimer’s through a visual context of presentation. Keep the following questions in mind before watching the video:
- What are some symptoms of Alzheimer’s?
- How do we diagnose Alzheimer’s?
- What are some potential treatments of Alzheimer’s? Can it be cured?
Before watching the video, take a minute to think about the questions above. Grab a pen and paper, and write down your answer to each of the questions above. Then, after watching the video, write down your answer for the questions again.
Having watched the video above, take a minute to think about your answers from earlier. Compare how different your answers are before and after watching the video. Did you learn anything new? Were you surprised with anything in the video? Were you curious about anything else that was not discussed? Keep those ideas in mind, because you will be tested on them soon!
Assessment
Assessment Process
- Quiz 1 (5 questions) – Alzheimer’s Stages (16.67%)
- Quiz 2 (5 questions) – Alzheimer’s Symptoms (16.67%)
- Quiz 3 (5 questions) – Alzheimer Treatment (16.67%)
- Test (15 questions) – Cumulative Examination (50%)
Note that if the student misses one or more quizzes, the weight will be added towards all other quizzes and exam. There will be no makeup quizzes so please do your best to do the course work.
To determine the learner’s final standing with the module, the learner will be tasked with creating a self-assessment to determine their overall grade for the module. To do this, the student will have to:
- Complete all quizzes and test.
- Count the number of questions you got correctly.
- Divide by the total number of questions (30, if no quizzes were missed).
Example:
- Quiz 1: 3/5
- Quiz 2: 2/5
- Quiz 3: 5/5
- Test: 12/15
Total: 3 + 2 + 5 + 12 = 22
Total: 22/30 = 73.33%
Assessments
This module features multiple activities in the form of Kahoot quizzes. Each of the following links will redirect students to a Kahoot test:
- The first test will examine the student’s ability to discern the stages of Alzheimer’s Disease development.
- The second test will test the student’s ability to identify symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease.
- Lastly, the third test will examine the student’s ability to comprehend treatments for Alzheimer’s Disease.
Kahoot Quiz 1: Alzheimer’s Stages
Kahoot Quiz 2: Alzheimer’s Symptoms
Kahoot Quiz 3: Alzheimer’s Treatment
Kahoot Final Test: Cumulative Test
The intended outcomes will have been met if students get a grade of 80% or higher on the aforementioned assessments. This module directly assesses the student’s grasp of Alzheimer’s Disease—from understanding its progression and stages, identifying and categorizing symptoms, and comprehending different treatment methods.
Formative Assessments
The course offers opportunities for feedback through the quizzes, each worth 16.67%, which students must complete in a timely manner online. The students will have a clear goal and success criteria throughout the course (formative assessment) to improve their learning.
According to Yale Poorvu Center For Teaching and Learning (2021), the quiz highlights potential misconceptions and learning throughout the course and addresses any learning gaps. The quizzes promote active recall, increasing student engagement and providing instant feedback to help students identify misconceptions and correct them immediately.
Summative Assessments
The summative assessment consists of 15 multiple choice questions that covers the topics of stages, symptoms, and treatment that was discussed throughout the course. Students will have access to the quizzes throughout the semester, allowing them to identify and correct misconceptions while preparing for the cumulative test worth 50% at the end of the course.
To earn course credit, the students must achieve a minimum grade of 50% and above. The final grade depends on the cumulative tests and individual formative assessments combined.
Roles and Responsibilities
| Name | Section | ||||||
| Bashar Kabd | Roles and Responsibilities & Assessment | ||||||
| Therese Taruc | Introduction & Assessment & References | ||||||
| Mansahaj Singh Popli | Assessment & References |
Bashar is responsible for creating the Kahoot Assessments and Assessment Process, Learning Activities, team communication and meeting planning, and assignment formatting. Mansahaj is responsible for the Assessment Plan, including Core Concepts, Learning Outcomes, and Sources for Study. Therese is responsible for the topic Introduction, including Overview, misconceptions, Rationale, Target Audience, Hosting, and Formative & Summative Assessments.
References
Alzheimer’s Association. (n.d.). Stages of Alzheimer’s. Alzheimer’s Association. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/stages
Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Alzheimer’s disease: Overview, symptoms, & treatments. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/9164-alzheimers-disease
DiSabato, D. J., Quan, N., & Godbout, J. P. (2016). Neuroinflammation: the devil is in the details. Journal of Neurochemistry, 139 Suppl 2, 136–153. https://doi-org.ezproxy.library.uvic.ca/10.1111/jnc.13607
Five stages of Alzheimer’s Disease. (n.d.). Research Gate. https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-stages-of-Alzheimers-disease_fig2_379727687
Kumar, A., Sidhu, J., Goyal, A., & Tsao, J. W. (2022, June 5). Alzheimer Disease. National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499922/
Mass General Brigham. (2024, August 16). Alzheimer’s Disease: Risk Factors, Testing, Treatments | Mass General Brigham [Video]. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ot1bea0-OXk&t=1s
Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (2023, June 7). Alzheimer’s stages: How the disease progresses. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/alzheimers-disease/in-depth/alzheimers-stages/art-20048448
National Institute on Aging. (2022, October 18). What Are the Signs of Alzheimer’s Disease? National Institute on Aging. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-symptoms-and-diagnosis/what-are-signs-alzheimers-disease
National Institute on Aging. (2023, April 5). Alzheimer’s Disease Fact Sheet. National Institute on Aging; National Institutes of Health. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-and-dementia/alzheimers-disease-fact-sheet
Tanwar, P. (2018). Use of Tactile Diagrams in Teaching Science to Visually Impaired Learners at the Upper Primary Level. Disability, CBR & Inclusive Development, 29(4), 109–116. https://doi.org/10.5463/DCID.v29i4.772
Yale Poorvu Center For Teaching and Learning. (2021). Formative and Summative Assessments. Yale.edu; Yale University. https://poorvucenter.yale.edu/Formative-Summative-Assessments
Recent Comments